Our Research
Research Topics
Oxidative stress pathways implicated in fetal programming
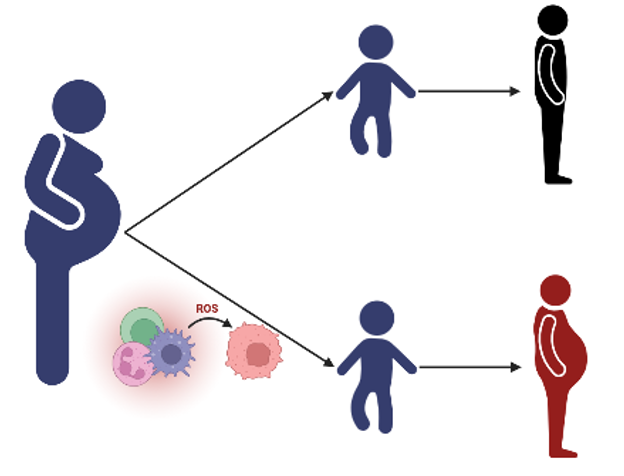
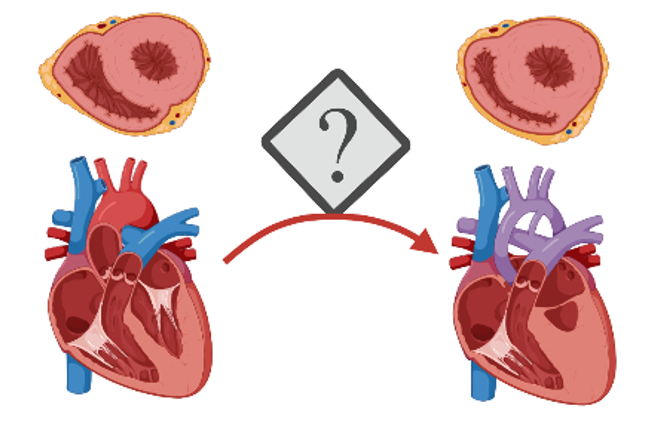
Cardiovascular disease and explicatory mechanism
Promoting healthy habits since the beginning of life

Search new strategies for new food ingredients
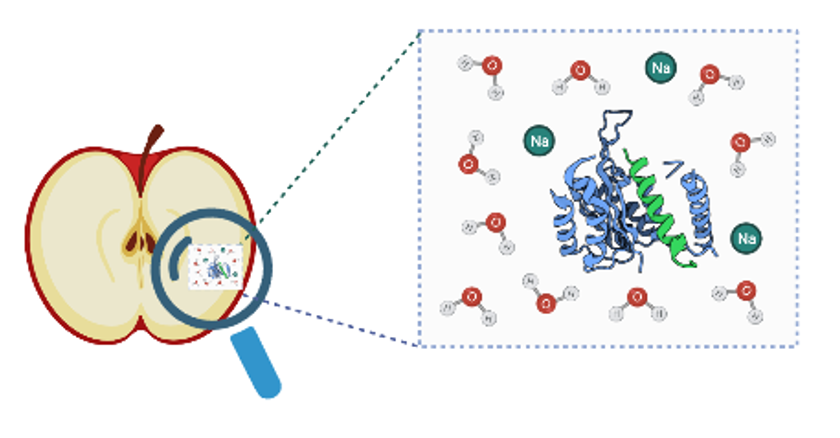
Improving health under nutritional approaches

Bioactivity of foods on cardiovascular health
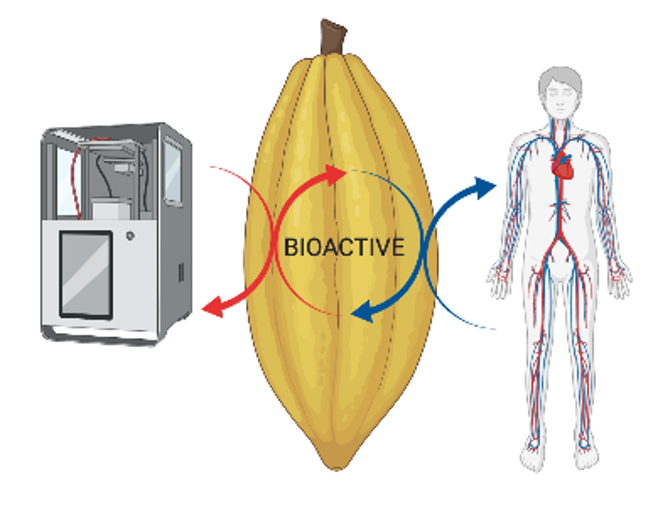
Competitive Projects
- Oxidative stress and fetal programming of cardiovascular disease (FEM2012-37634-C03-01)
2013 – 2016
Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Spain)
- Effect of supplementation with DHA on oxidative stress associated with low birth weight (FEM2015-63631-R)
2016 – 2019
Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Spain)
- Sustainable coffee production and consumption: validation of by-products as food ingredients (AGL2014-57239-R)
2015 – 2018
Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Spain)
- Antioxidant ingredients from coffee as a strategy to reprogram cardiometabolic disease through lactation (ARTI2018-097504-B-I00)
2019 – 2021
Ministry of Science (Spain)
Industry-Transferency Projects
- Validation of new food ingredients for the development of anti-obesity nutraceuticals (PFTC-19)
2019 – 2020
Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (Spain) - AORA Health S.L. Company
- Characterization of Bioactive Compounds in Breast Milk for the Improvement of Infant Formulas (PFTC-20)
2020 – 2022
Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (Spain) - Alter Farmacia S.A.-Nutribén Company
Networking Cooperation Projects
- Creation of basic research lines with National University of Singapore (2011/ASIA/01)
2011 – 2012
Santander Bank (Spain) - Singapore
- Interuniversity network in nutrition and perinatal health (2015/EEUU/01)
2015 – 2016
Santander Bank (Spain) - USA
- Strategy for the design of sustainable food ingredients (2017/EEUU/01)
2017 – 2018
Santander Bank (Spain) - USA
Articles
Food Technology & Developmental of New Ingredients
Intake of bean sprouts influences melatonin and antioxidant capacity biomarker levels in rats
Kidney bean sprouts could be a good source of dietary melatonin and other bioactive compounds known to have health benefits.
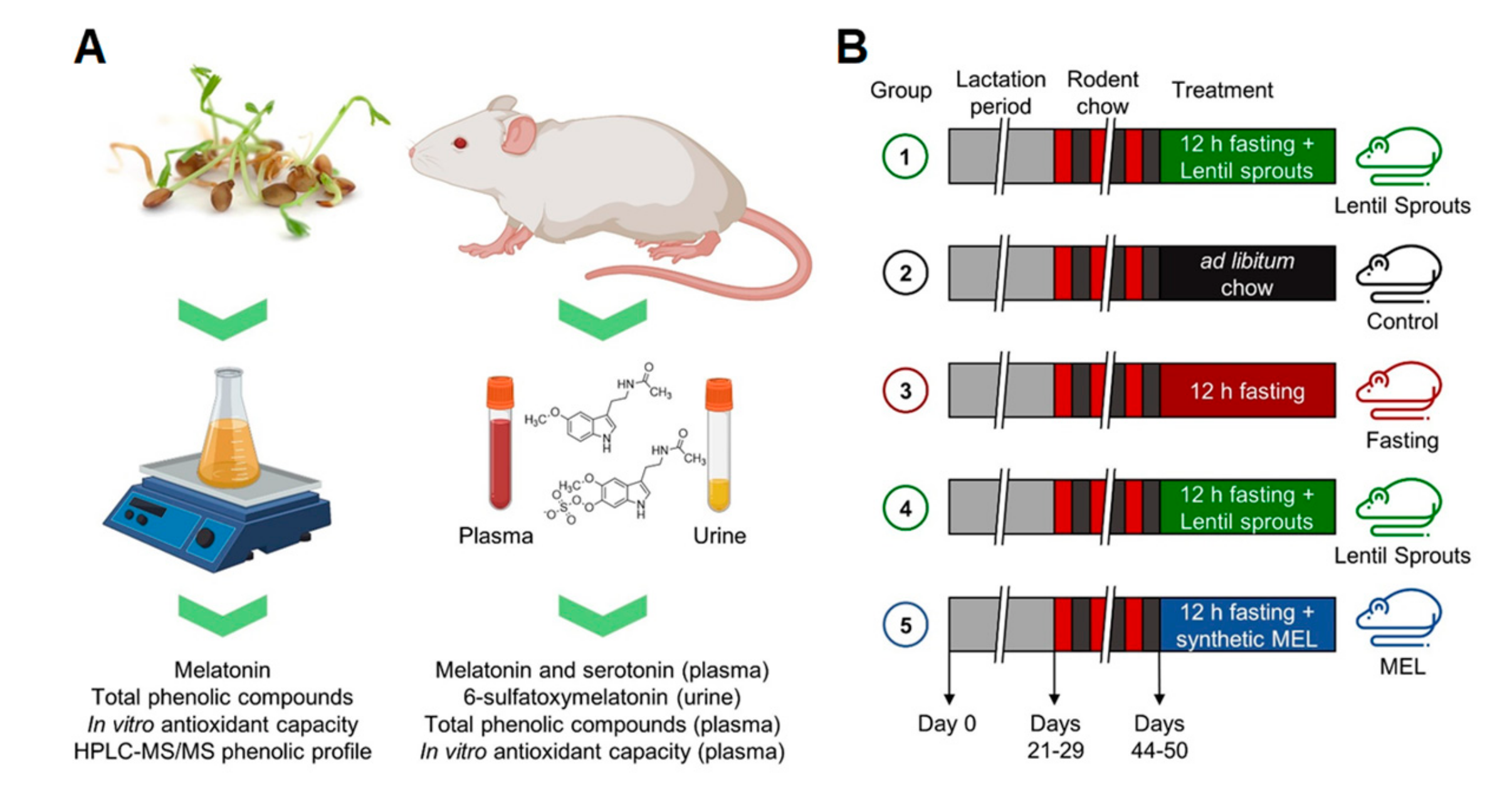
We investigated the bioavailability of melatonin from lentil sprouts and its role in plasmatic antioxidant status. Their intake could increase melatonin plasmatic concentration and attenuate plasmatic oxidative stress.
Teas and herbal infusions as sources of melatonin and other bioactive non-nutrient components
The teas and herbal infusions could be consided as suitable drinks herein validated for their bioactive compounds that may act as antioxidants and non-protein inhibitors of digestive enzymes.
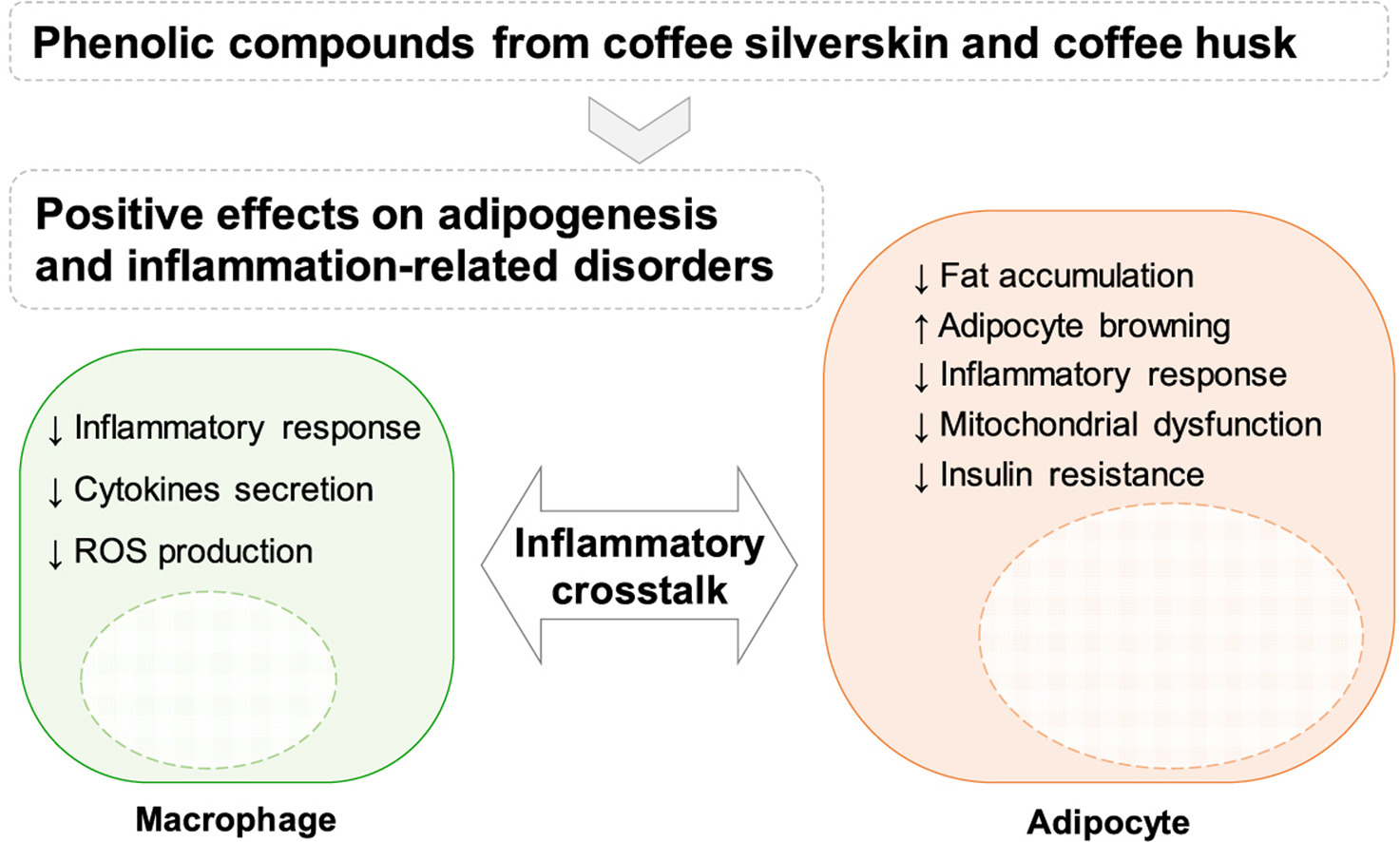
Coffee silverskin and husk are beneficial in reducing adipogenesis and inflammation-related disorders.
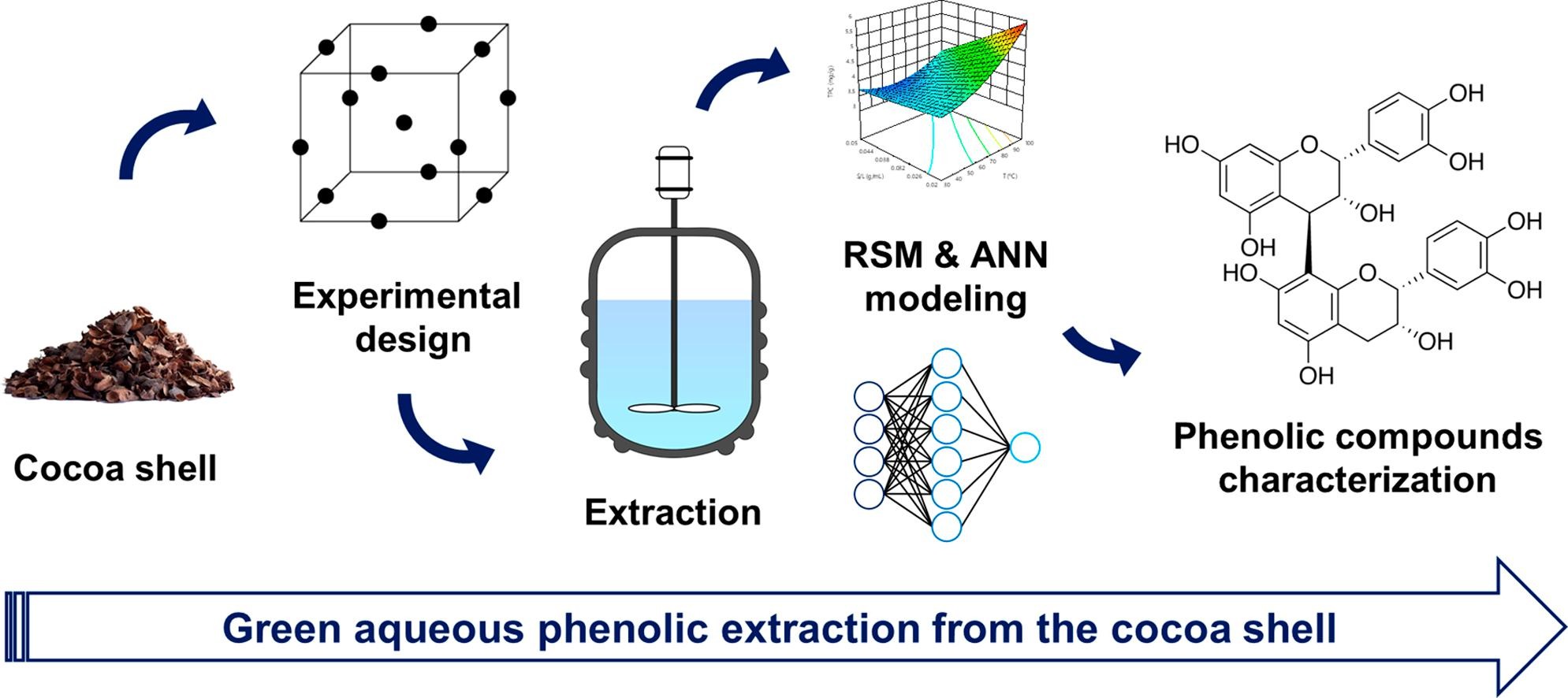
Green extraction of phenolic compounds from the cocoa shell was modeled and optimized.
Potential application of a useful, clean, environmentally friendly and cost-effective method to recover phenolic compounds from coffee parchment and to revalorize the by-product by converting it into high-added value new products to be used in the food.
These black bean coat aqueous extracts and powders might represent natural alternatives to synthetic colorants, ecologically extracted, and with a high antioxidant potential.
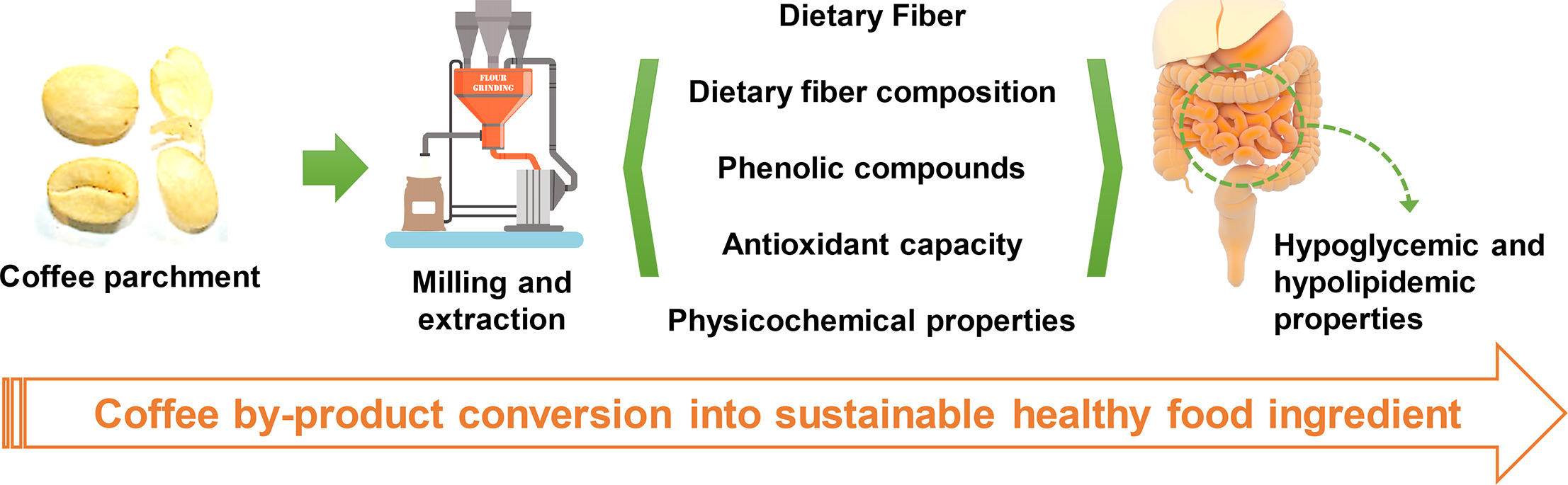
Coffee parchment as a new dietary fiber ingredient: Functional and physiological characterization
Milling is a strategy for developing fiber-rich coffee parchment-based ingredients. Coffee parchment shows promising hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic capacities.
The melatonin-enriched foods exhibited potent free radical scavenger and antioxidant functions that may be used as a nutritional strategy to alleviate chronic and age-related diseases.
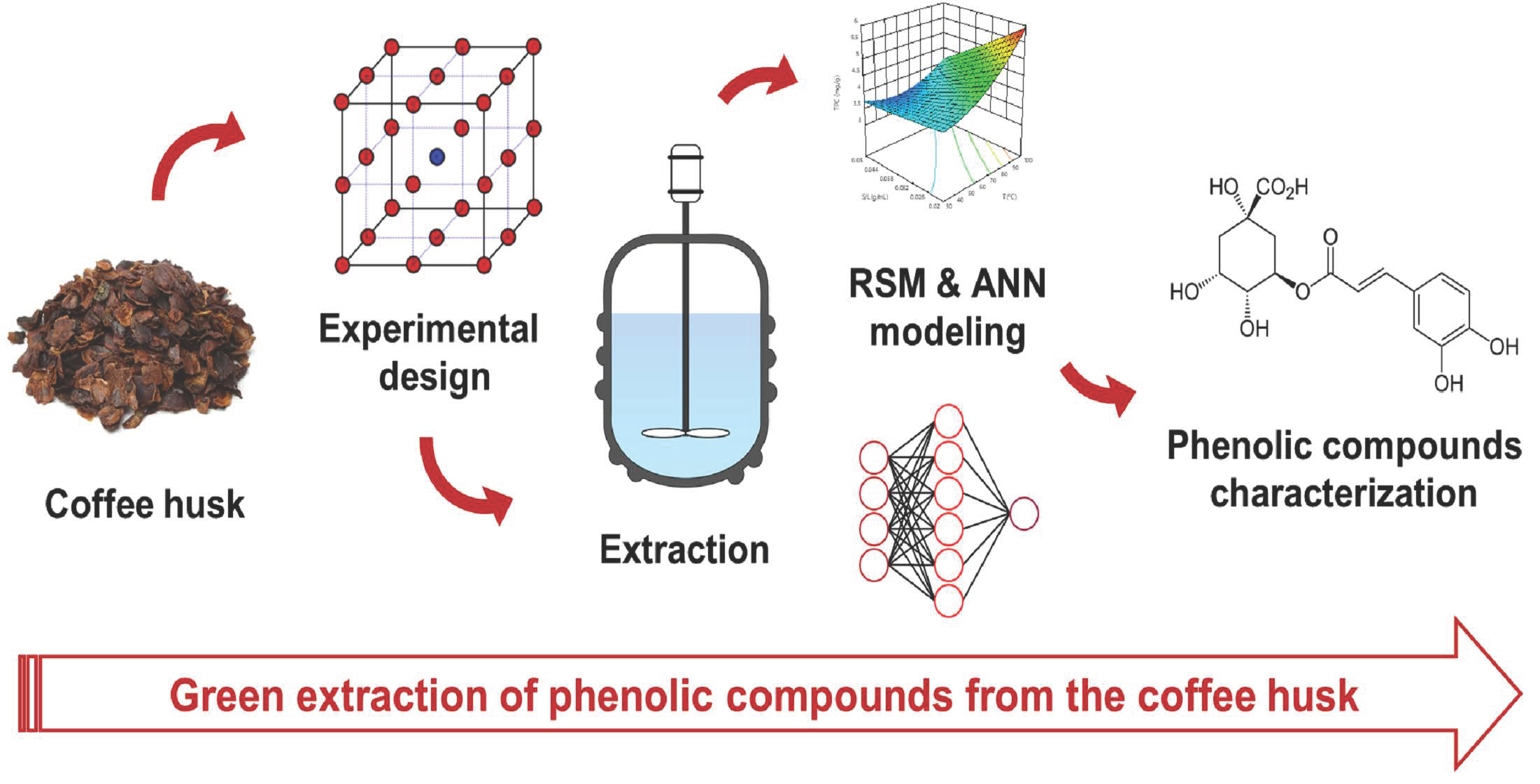
The phenolic aqueous extracts from the coffee husk could be used as sustainable food ingredients and nutraceutical products.
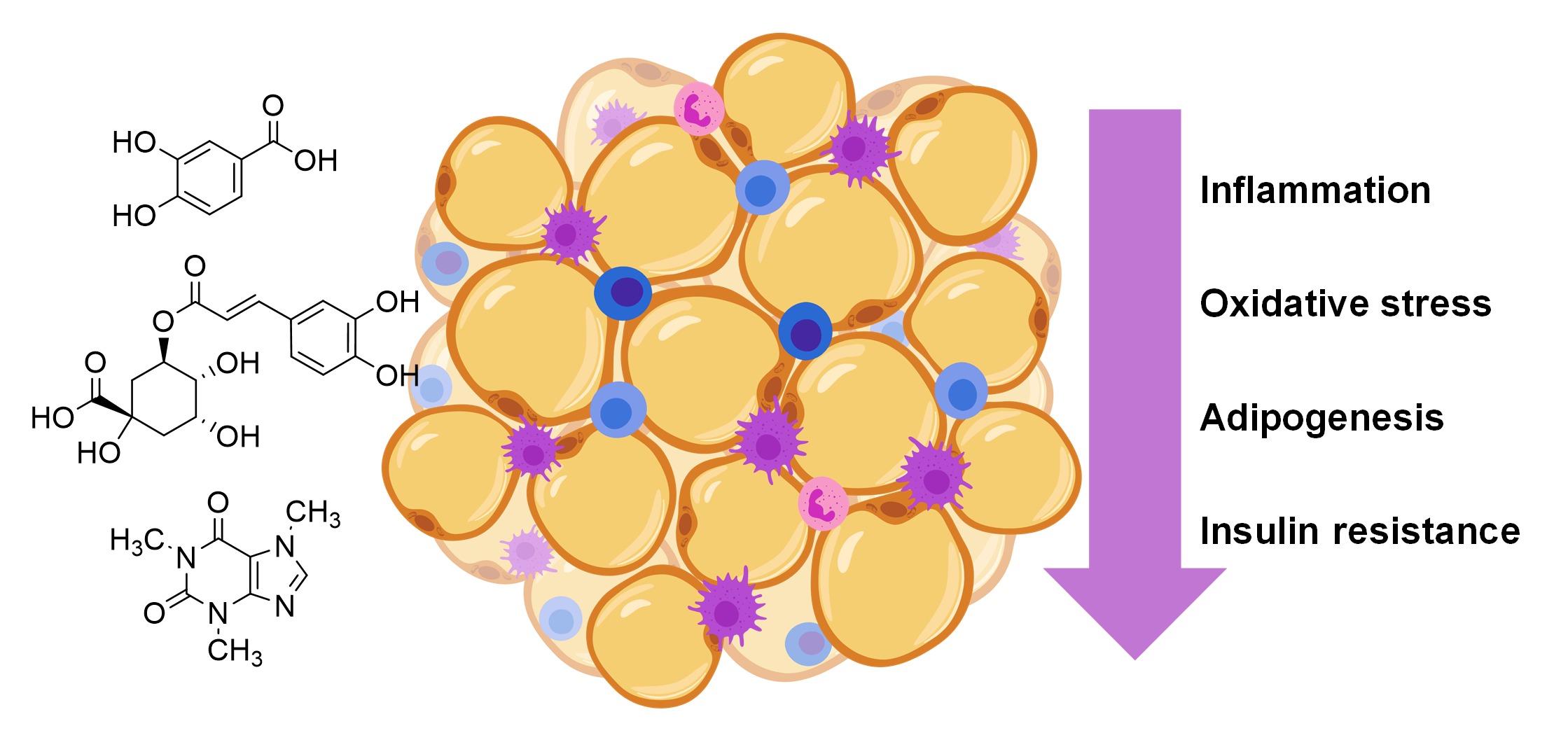
We identified the phytochemicals from coffee and cocoa by-products and offered new insights into their associations with biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress, adipogenesis, and insulin resistance in vitro.
Cocoa shell phenolics promote a beige phenotype in adipocytes. Macrophages-adipocytes inflammatory interaction is reduced preventing mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance.
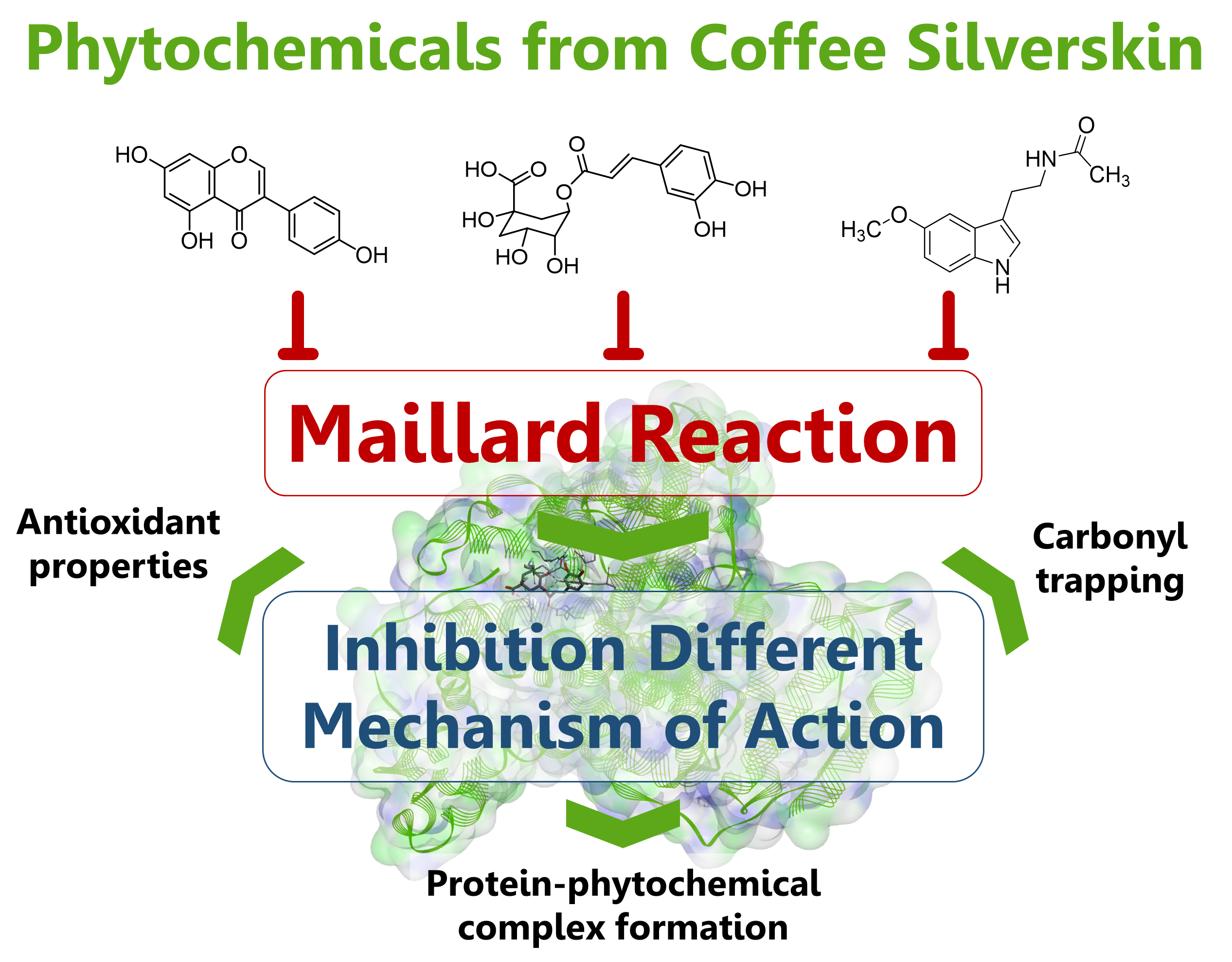
Isoflavones and melatonin may contribute to the antiglycative/antiglycoxidative properties associated with coffee silverskin.
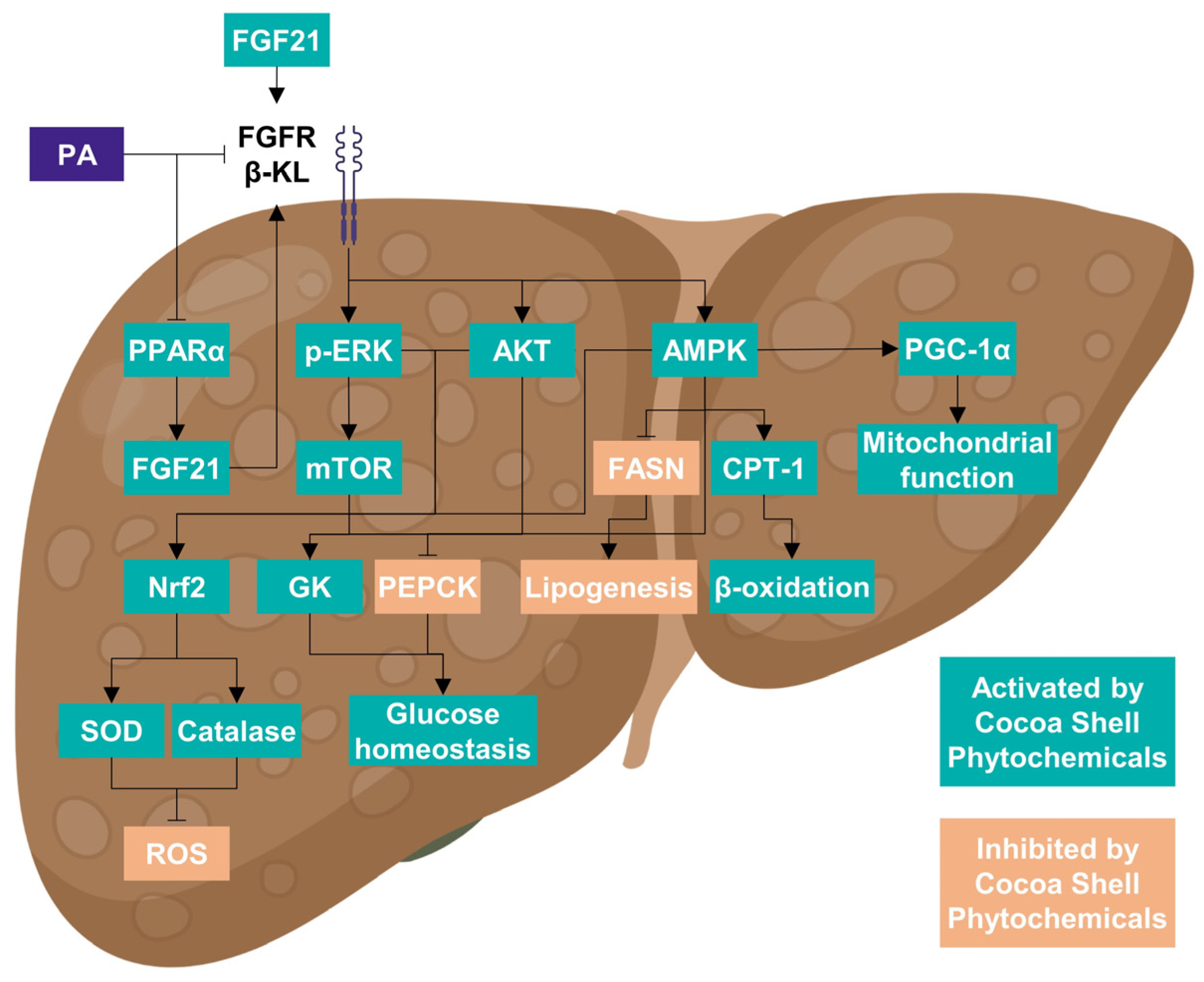
The cocoa shell phytochemicals are proved to modulate FGF21 signaling. Results demonstrate the in vitro preventive effect of the phytochemicals from the cocoa shell on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Gestational Health & Pregnancy Epidemiology
In early gestation, low antioxidants were associated with development of complications.
We showed an association between red blood cells, hematocrit, malondialdehyde, and nitrates with preeclampsia in twin pregnancies.
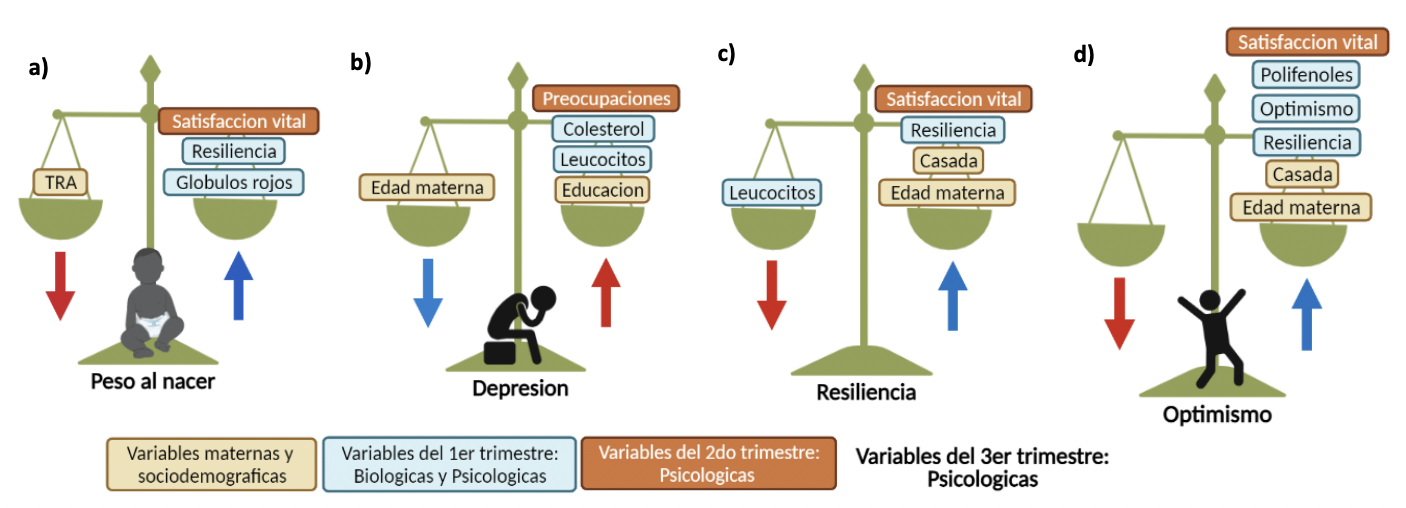
The relevance of psychological health during pregnancy for maternal and neonatal outcome, and to consider it in preventive policies in OBS/GYN.
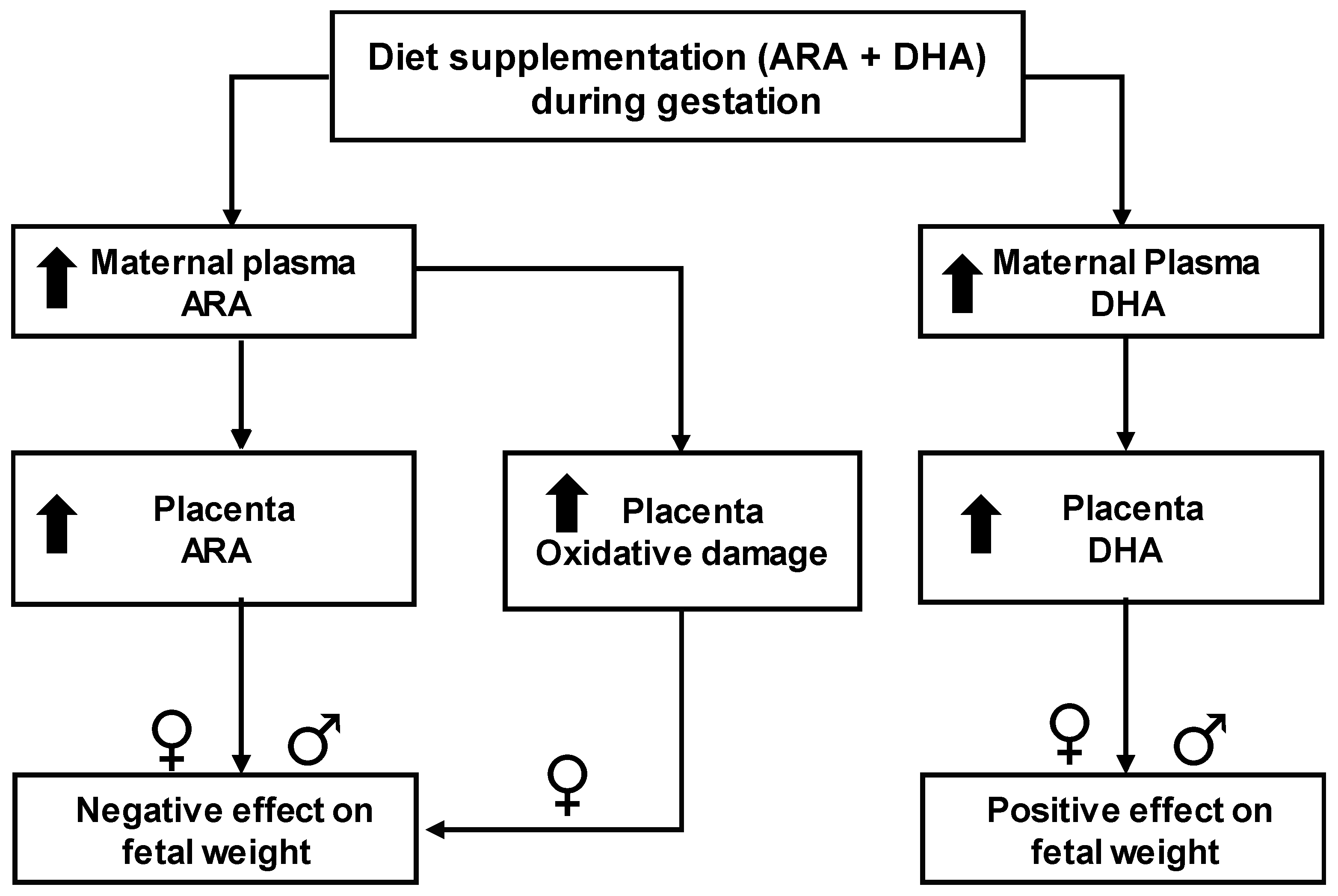
High arachidonic acid during gestation associates with intrauterine growth restriction, through placental oxidative stress, with females being more susceptible.
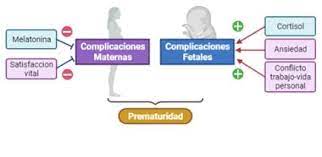
Maternal Psychological and Biological Factors Associated to Gestational Complications
High maternal melatonin and life satisfaction could be protective factors against the maternal complications during pregnancy. Low anxiety and cortisol and reduced work–life conflicts could prevent fetal complications.
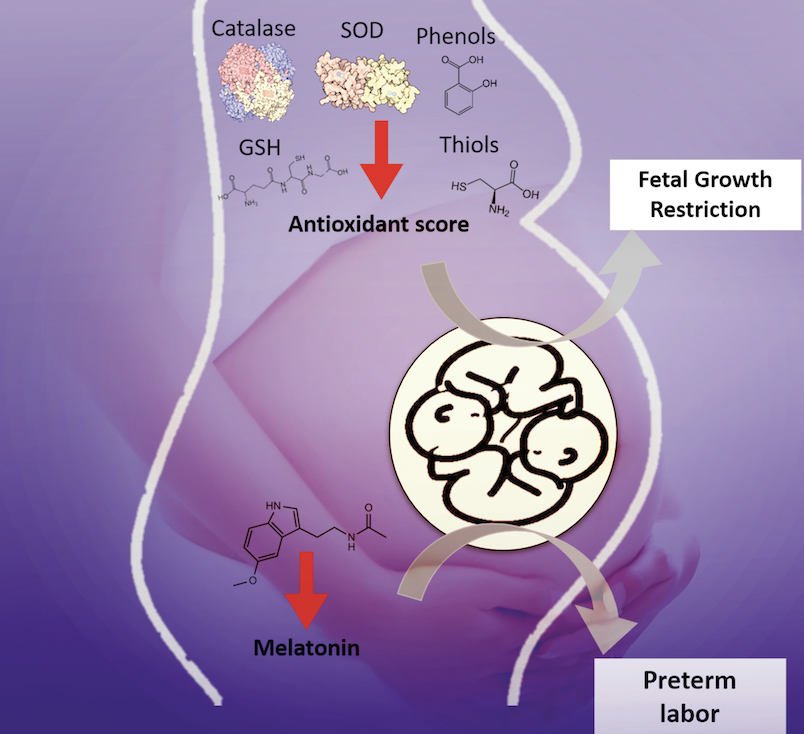
In twin gestations, maternal antioxidants and melatonin could be biomarkers to be included in algorithms to predict fetal growth restriction and preterm labor.
Fetal Programming of Cardiovascular Disease: Sex differences & Maternal Undernutrition
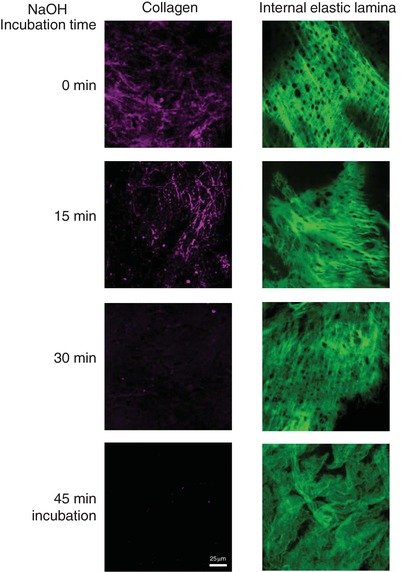
Fetal undernutrition induces similar aortic structural and mechanical alterations in young male and female rats. Our data argue against an early mechanical cause for the sex differences in hypertension development.
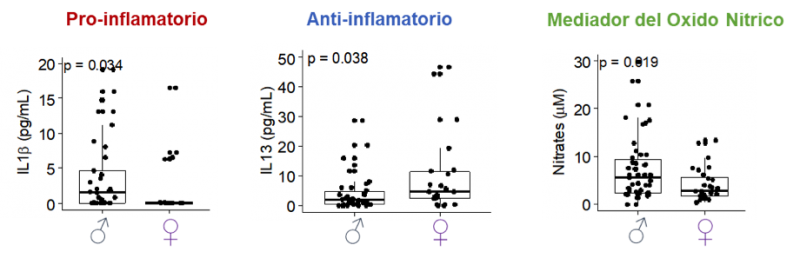
Women with a male fetus may have a worse capacity to counteract an inflammatory response. They may have better vasodilator capacity, but in the presence of an oxidative environment, a higher nitrosative damage may occur.
Low birth weight (LBW) and accelerated growth during lactation are associated with cardiometabolic disease development. LBW offspring from rats exposed to undernutrition during gestation develops hypertension. We tested if slower postnatal growth improves early cardiometabolic alterations.
Fetal undernutrition is associated with perinatal sex-dependent alterations in oxidative status
Adult males with maternal undernutrition (MUN) during gestation were hypertensive and exhibited the higher carbonyl levels compared to Controls. Adult MUN females were normotensive and did not exhibit differences in any of the biomarkers.
Long term effects of fetal undernutrition on rat heart. Role of hypertension and oxidative stress
During perinatal life, females exposed to fetal undernutrition are protected from cardiac alterations, but in ageing they exhibit ventricular hypertrophy and functional loss. The severity of cardiac damage might be greater in males due to hypertension.
This study was designed to evaluate the influence of sex on BM composition during the first month of lactation, focused on macronutrients and antioxidants.
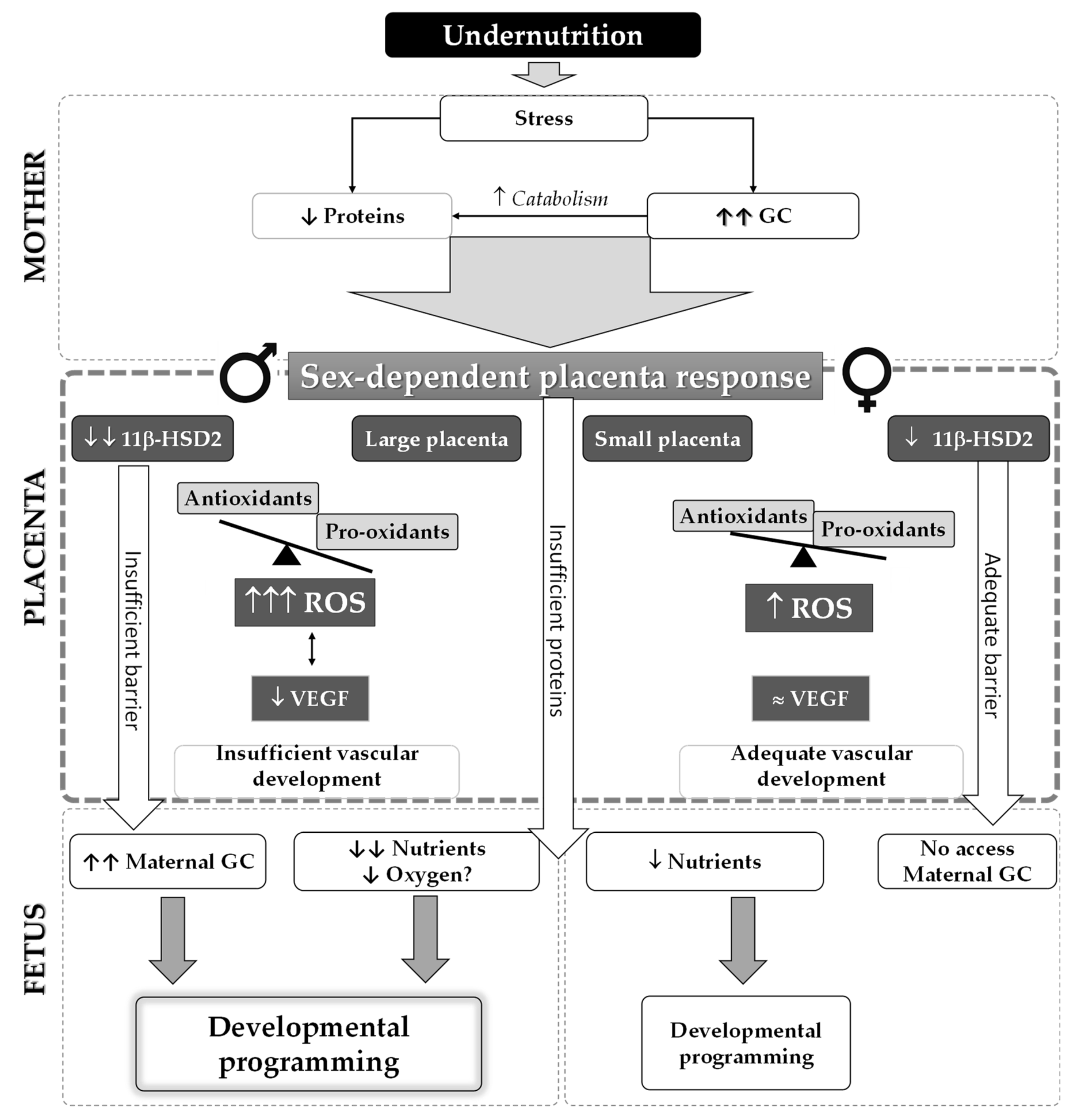
Male placenta has worse adaptation to undernutrition with lower efficiency, associated with oxidative disbalance and reduced vascularization and glucocorticoid barrier.
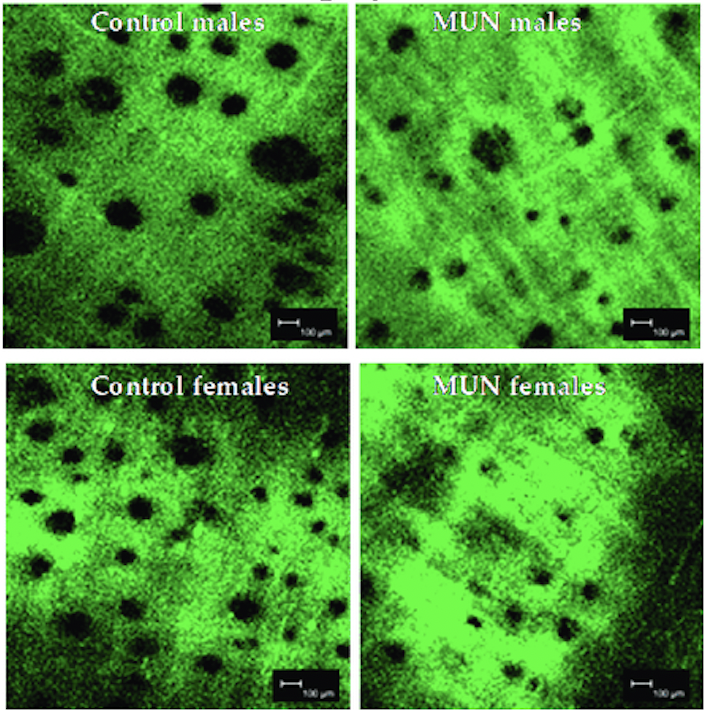
Fetal undernutrition induces resistence artery inward eutrophic remodeling and stiffness in both sexes. Resistance artery structural and mechanical alterations can participate in the development of hypertension in aged females.
General Nutrition & Healthy Habits in Lactation Period: Nutrition & Psychological Stage
AP-Q is a questionnaire to assess healthy food pyramid adherence, easy to complete, cost-effective, timesaving and has the competency to assess, besides diet, several features affecting health status.
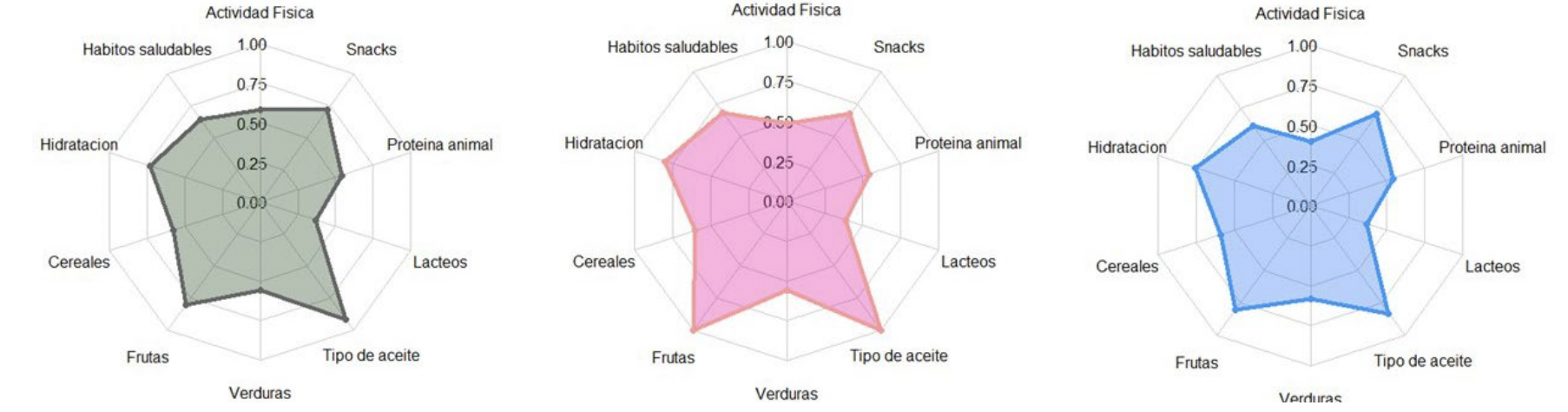
Assessment of Adherence to the Healthy Food Pyramid in Pregnant and Lactating Women
Breastfeeding mothers of young age and low socioeconomic/educational level would be the target population to carry out nutritional interventions that improve their adherence to the Healthy Foos Piramyd.
Breast milk antioxidants are linked to gestational age providing higher levels to infants with lower maturation; maternal ageing has a negative influence on melatonin.
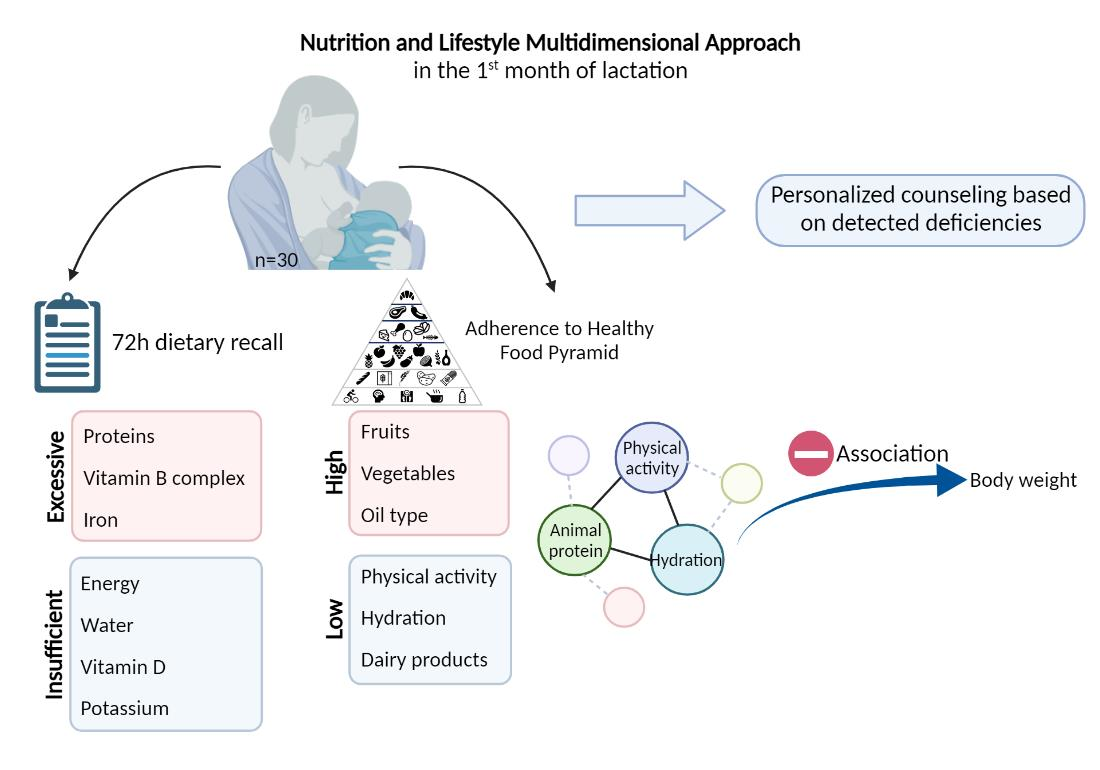
During the 1st month postpartum, breastfeeding women exhibited nutritional imbalances and poor physical activity negatively influencing anthropometric parameters.
Healthcare professional counseling is essential during the breastfeeding period, particularly in vulnerable mothers with preterm delivery.
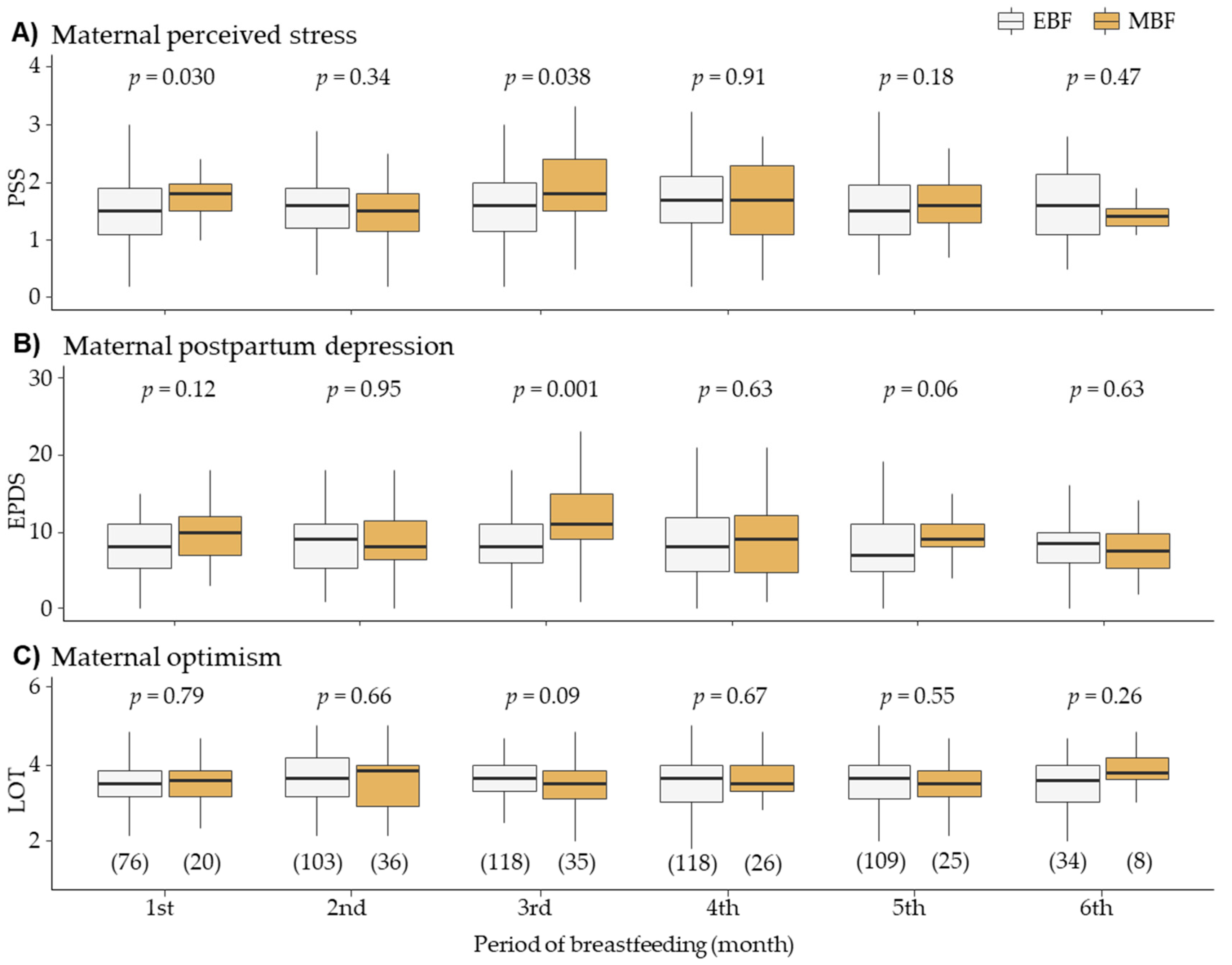
In the 3rd month of breastfeeding, women with mixed breastfeeding exhibited higher stress and depression compared to those with exclusively breastfeeding. Evaluation of maternal psychological concerns and providing support to lactating mothers may help improving breastfeeding adherence.
Plasma Oxidative Status in Preterm Infants Receiving LCPUFA Supplementation: A Pilot Study
ARA:DHA supplementation in preterm neonates resulted in an improvement in antioxidant to oxidant balance and a decrease in early fatty acid precursors of the n-6 relative to the n-3 pathway. These effects may reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
Diet had a larger influence than the maternal body’s composition on BM fatty acids during the first month of lactation, demonstrating a better adherence to the HFP and positively impacting on the omega-3 content in BM, a fact that is modulated by one’s maternal age.
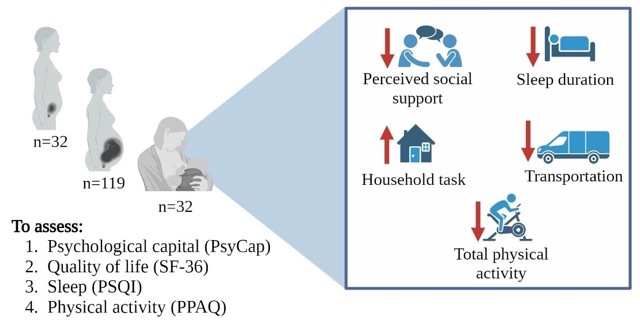
Women during Lactation Reduce Their Physical Activity and Sleep Duration Compared to Pregnancy
During lactation, the poorer sleep and physical activity, together with a lower social support of the woman, may lead to deficient mental health adjustment.
Nutrition During Neonatal Period
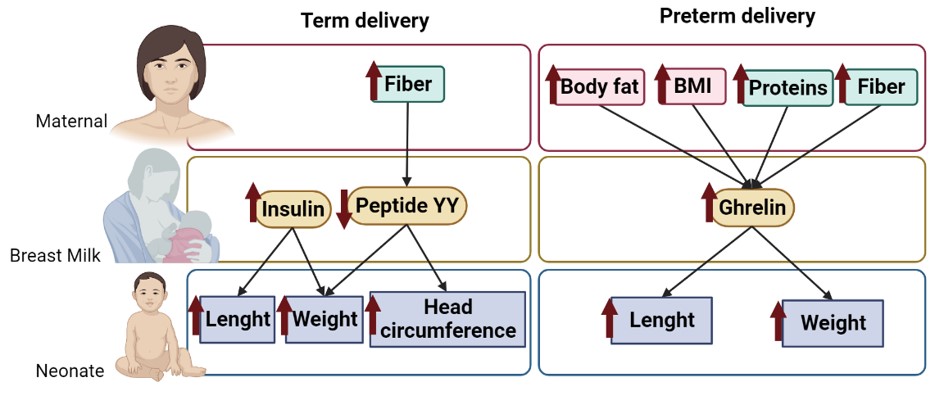
Preterm labor is a factor influencing the levels of BM hormones. Ghrelin is lower in BM from women with preterm labor and is associated with maternal fat and diet, our data support the monitoring of women diet and body composition.
Models to Explore Cardiovascular Health
Cocoa Shell Extract has vasodilatory properties associated with increased nitric oxide bioavailability, related to its antioxidant phytochemicals. Cocoa Shell Extract is a potential food ingredient for diseases related to endothelial dysfunction.
Reviews
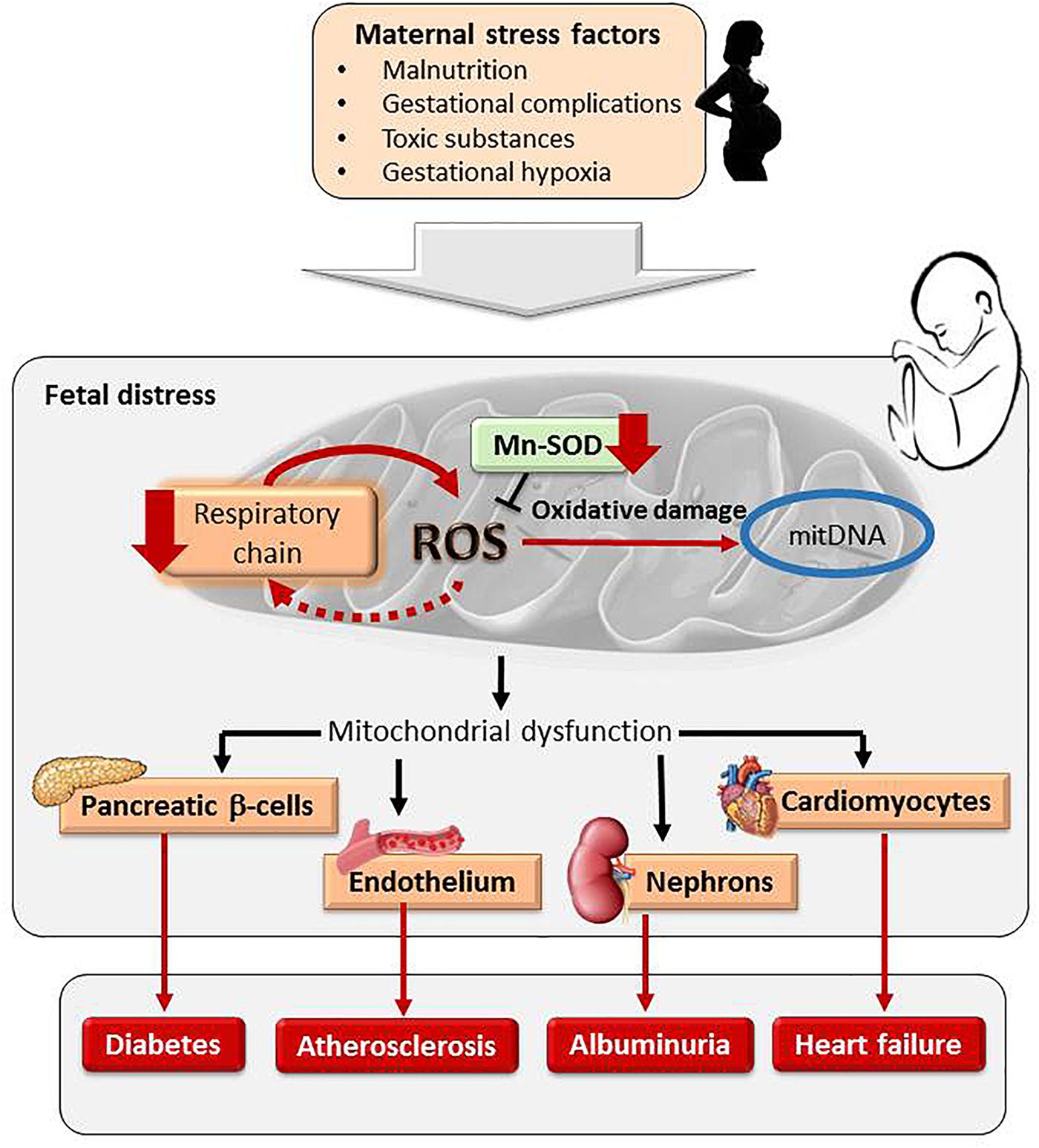
Implication of Oxidative Stress in Fetal Programming of Cardiovascular Disease
This review summarize the alterations in oxidative balance in fetal stress factors covering: the evidence from human studies of low birth weight, and the specific redox alterations in cardiovascular control organs induced by exposure to stress factors.
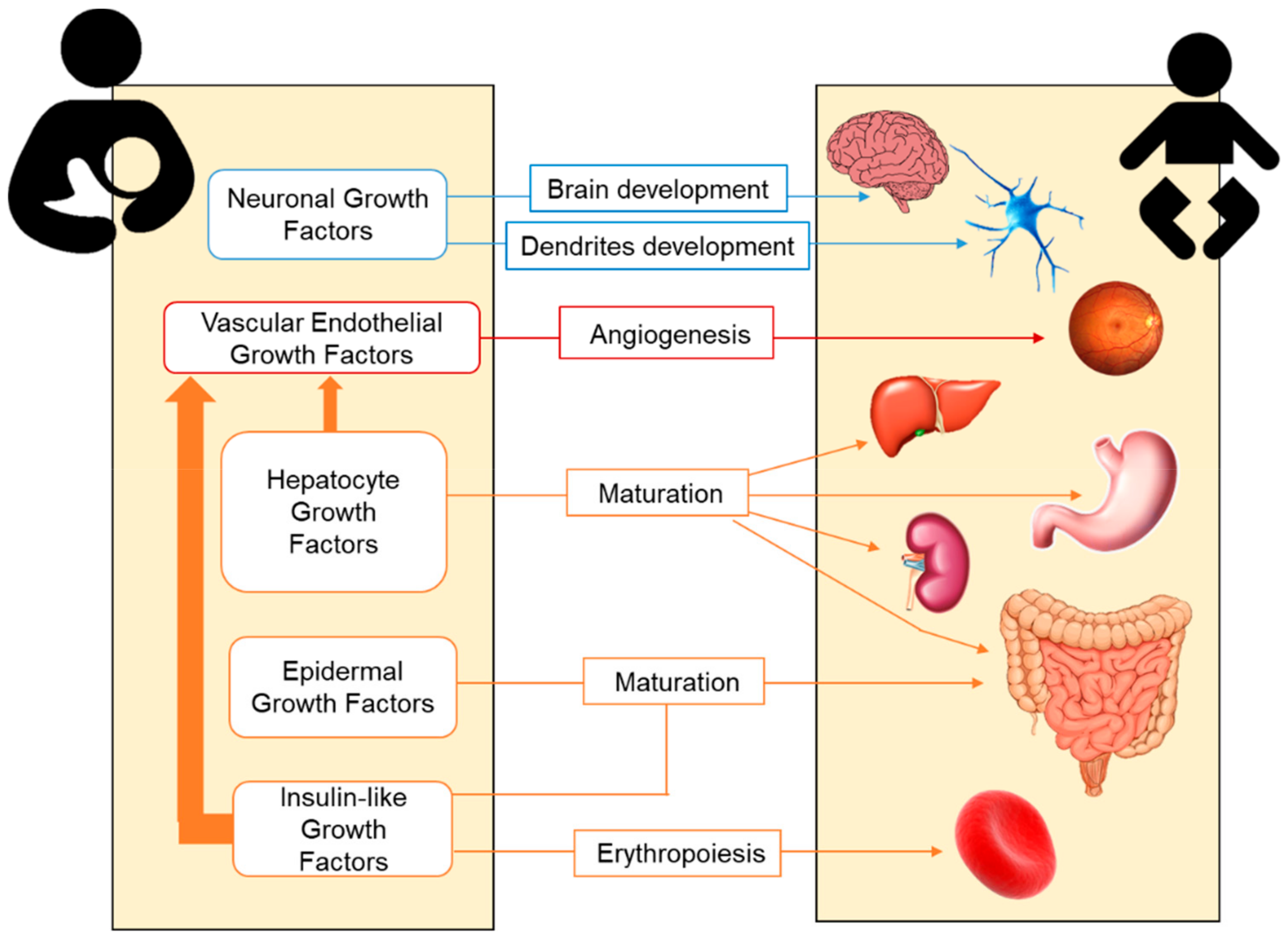
A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity
The aim of the review is to summarize the knowledge regarding bioactive factors present in breastmilk, namely antioxidants, growth factors, adipokines, and cytokines, paying attention to prematurity.
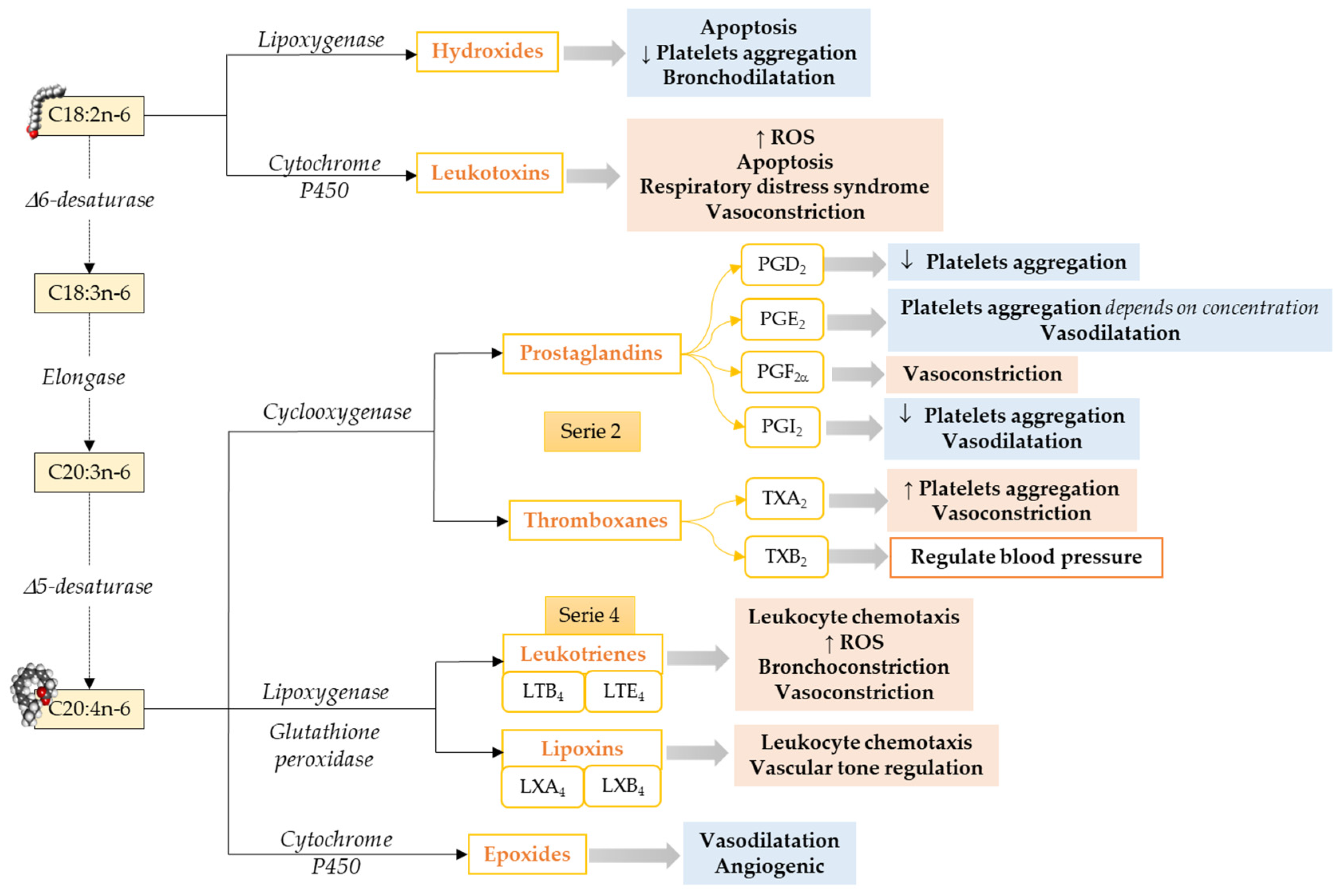
Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Neonatal Cardiovascular Physiology and Diseases
In this review, we discuss LCPUFAs metabolism, SPMs, and their effect on cardiovascular health and diseases primarily focusing in neonates.
Collaborations
Women Aged over 40 with Twin Pregnancies Have a Higher Risk of Adverse Obstetrical Outcomes
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18(24), 13117
Younger Age in Adolescent Pregnancies Is Associated with Higher Risk of Adverse Outcomes
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18(16), 8514
Maltodextrin-induced intestinal injury in a neonatal mouse model
Dis Model Mech. 2020, 13(8), dmm044776
J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11(20), 6192
J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12(6), 982
Maternal Obesity in Twin Pregnancy: The Role of Nutrition to Reduce Maternal and Fetal Complications
Nutrients 2022, 14(7), 1326


